Brief Discussion on New Process of Electroplating Wastewater Treatment
Abstract: Electroplating is one of the three major polluting industries in the world. If it is discharged without treatment, it will seriously pollute our living environment and be a great waste of resources. In this paper, the new process of electroplating wastewater treatment was analyzed by the experiment of “micro-electrolysis-neutralization-coagulation and sedimentation†treatment of acidic electroplating wastewater containing Cr6+, Ni2+ and Cu2+.
Electroplating wastewater contains many types of pollutants, high toxicity, serious damage, heavy metal ions or cyanide, and some of them are highly toxic substances that cause cancer, teratogenicity or mutagenicity. They are extremely harmful to humans. Electroplating wastewater is affected by plating and process. Different, the types of pollutants are also different, the concentration difference is large, the composition is complex, not only contains a large number of heavy metal ions such as Cr6+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Fe2+, Ni2+, but also contains highly toxic CN-. In addition, electroplating wastewater contains a large amount of valuable metals, such as improper treatment, discharged into the natural system, both polluting the environment and wasting resources.
At present, the traditional domestic treatment methods for Cr6+ electroplating wastewater are chemical reduction method, electrolytic reduction method, ion exchange method and the like. Inspired by the test of heavy metal wastewater by Gu Yugang and others, the author experimented with the wastewater treatment of the plant and developed a new process for electroplating wastewater treatment of “micro-electrolysis – neutralization – coagulation sedimentationâ€.
1·Processing process
1.1 Process flow
Process flow, see Figure 1.
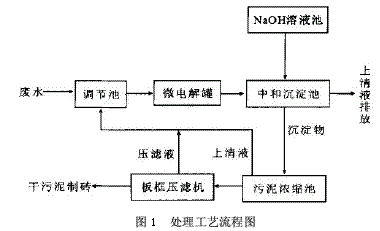
1.2 Process Introduction
The filler in the micro-electrolysis tank is 1:1 cast iron scrap and coke. When the acidic waste water passes through the filler in the micro-electrolysis tank, the low potential Fe and the high potential C generate a potential difference in the waste water, forming numerous micro-primary batteries. The electrode reactions are mainly the following two types:
Anode: Fe-2e→Fe2+, cathode: ZH++2e→H2↑ The Fe2+ formed in the reaction reduces Cr6+ to Cr3+, and the reaction formula is as follows: CrO42-+3Fe2++4H+→Cr3++3Fe3++4OH- After the reaction, the wastewater enters the neutralization sedimentation tank, and the neutralization precipitate is a batch reaction. When the wastewater reaches the predetermined water level of the neutralization sedimentation tank, the water is stopped, and the NaOH solution is controlled by the pH meter and the PLC system, and the mixture is stirred to control the wastewater. The pH value is in a suitable range. Under this condition, Cr3+, Cr2+, Ni2+, Fe3+ form a flocculant precipitate of hydroxide. After standing for 1 hour, the supernatant is discharged to the standard, and the sludge enters the sludge concentration tank. After the filter press is filtered, the mud cake is transported to the brick factory for brick making.
1.3 Process conditions for wastewater treatment
In order to ensure the discharge of the electroplating wastewater after treatment, the micro-electrolysis-neutralization-coagulation precipitation experiment was carried out on the wastewater treatment to determine the design process conditions. The raw water used for the experiment was pH=2.85, [Cr6+]= 25.1 mg/L, [total Cu] = 128 mg/L, [total Ni] = 26.2 mg/L.
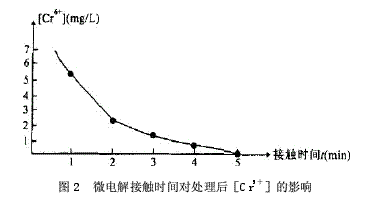
1.3.1 Effect of microelectrolysis contact time on reduction of Cr6+
When the Cr6+-containing wastewater passes through the micro-electrolysis tank, an electrode reaction occurs and is reduced to Cr3+. The author conducted an experiment on the relationship between the microelectrolysis contact time and the treated [Cr6+], as shown in Fig. 2. Through experiments, when the contact time is greater than 5 min, the treated [Cr6+]<0.5 mg/L.
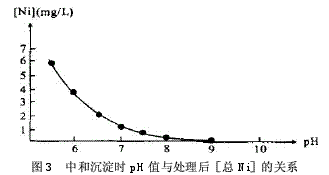
1.3.2 Determination of pH value during neutralization precipitation
The pH values ​​of the hydroxide precipitates of various metal ions are different. Because the electroplating mixed wastewater coexisting ion system is very complicated, it is necessary to satisfy the actual test results to meet the requirements of the actual test results. The Ksp of Ni(OH)2 is 1.6×10-14. The pH value is the highest among the three ions of Cr3+, Ni2+ and Cu2+. The experiment of the relationship between pH and [total Ni] concentration after neutralization precipitation is shown in the figure. 3, through the experiment, after the treatment of effluent pH> 7.5, [total Ni] <1.0mg / L. According to the experiment of the relationship between the microelectrolysis contact time and the treated [Cr6+] and the experiment of the relationship between the pH and the [total Ni] concentration after the neutralization, the contact time in the treatment process was set to 10-20 min, and the pH of the precipitate was neutralized. The value is controlled between 7.5 and 8.5.
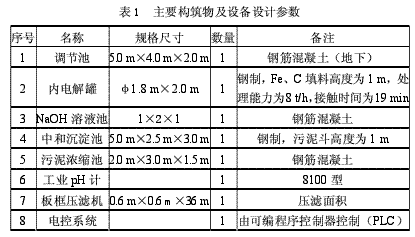
2. Main structures and equipment
The main structure and equipment design parameters are shown in Table 1.
3. Acceptance monitoring results
After three months of trial operation, the plant's sewage treatment station was inspected and monitored by the environmental monitoring station on November 4-6, 2009. The monitoring results and emission standards were in compliance with the "Sewage Integrated Emission Standard" (GB89782-1996 second time). The paragraph level standard), it can be seen that the indicators of the effluent have reached the standard.
4 Conclusion
The electroplating industry must proceed from reality, continuously improve the scientific and technological content, select appropriate wastewater treatment methods, eliminate environmental pollution, and adopt the comprehensive utilization of resources to take the road of sustainable development and realize social, economic and environmental benefits. Unite. This project uses Fe-C micro-electrolysis to treat mixed wastewater containing Cr6+ electroplating. It is a new type of treatment process. It reduces the Cr6+ by the action of Fe-C micro-electrolysis. It does not need to increase the reducing agent and reduce the processing cost. Intermittent treatment is used for neutralization and sedimentation, which is convenient for operation and management, and has good effect, which can ensure stable discharge of wastewater after treatment.
Today's attention: http://news.battery.com.cn/show-29464/
Http://news.battery.com.cn/show-29467/
AS Jars
5 G Round Shape Jar,As Jars,Cosmetic Acrylic Jar,Cream Care Jar
Zhejiang Xinlei Packaging.Co.Ltd.(China) , https://www.xinleipack.com