
Finned tubes are used in applications where heat needs to be transferred from a hotter liquid to a cooler liquid through the tube walls. The efficiency of heat transfer depends on various factors including the temperature difference between the two liquids, the heat transfer coefficient between the liquids and the tube walls, and the surface area exposed to each liquid.
Table of Contents
- What is a Finned Tube?
- Different Types of Finned Tubes
- Why Are Finned Tubes Made of Aluminum?
- Working Principle of Finned Tube Heat Exchangers
- Low Fin Tube Dimensions
- Applications of Helical Solid Finned Tubes
- Benefits of Using Fin and Tube Heat Exchangers
- Features of G-Type Finned Tubes
- Quality Assurance for Stainless Steel Finned Tubes
- Size Range of G-Type Fin Tubes
- Classification of Finned Tubes by Process and Fin Shape
- Comparison: High Fin Tubes vs. Low Fin Tubes
- Causes of Leaks in Low Fin Tubes
- Factors Influencing Heat Transfer in Low Fin Tubes
What is a Finned Tube?
A finned tube is essentially a long tube with fins attached to its outer surface, functioning as a heat exchanger. These fins serve as a medium for transferring heat, allowing energy to move from the exterior to the interior and vice versa. They are key components in heat exchangers, facilitating efficient heat exchange between thermally conductive fluids.
Explore Different Types of Fin Tubes for Heat Exchangers
The following table provides an overview of some essential types of fin tubes used in heat exchangers. This information should help you determine which type best suits your specific needs and applications. Understanding these options will ensure optimal performance based on intended use.
Different Types of Finned Tubes
| Fin Type |
Icon |
Tube Material |
Fin Material |
Fin Height |
Fin Thickness |
Tube Diameter |
| Plain Finned |
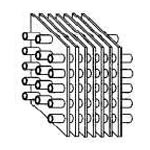 |
Carbon steel, stainless steel, copper, aluminum |
Aluminum, copper, stainless steel |
6-25 mm |
0.2-0.6 mm |
12.7 mm (1/2") to 63.5 mm (2.5") |
| L-Finned |
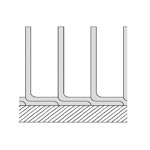 |
Carbon steel, stainless steel, copper |
Aluminum, copper, stainless steel |
6-19 mm |
0.3-0.5 mm |
15.9 mm (5/8") to 38.1 mm (1.5") |
| G-Finned |
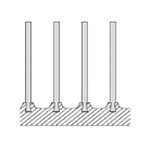 |
Carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel |
Aluminum, copper |
6-15 mm |
0.3-0.5 mm |
15.9 mm (5/8") to 50.8 mm (2") |
| Extruded Finned |
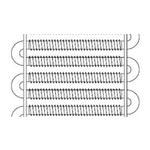 |
Aluminum, copper |
Aluminum |
8-16 mm |
0.4-1.2 mm |
12.7 mm (1/2") to 31.8 mm (1.25") |
| U-Tube Finned |
 |
Carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel |
Aluminum, copper, stainless steel |
6-25 mm |
0.3-0.5 mm |
15.9 mm (5/8") to 38.1 mm (1.5") |
| Studded Finned |
 |
Carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel |
Carbon steel, alloy steel |
10-50 mm |
6-12 mm |
25.4 mm (1") to 114.3 mm (4.5") |
| Helical Finned |
 |
Carbon steel, stainless steel, copper, aluminum |
Aluminum, copper, stainless steel |
8-16 mm |
0.3-0.5 mm |
12.7 mm (1/2") to 76.2 mm (3") |
Reference Sizes and Uses of Finned Aluminum Tubing
Finned aluminum tubing is typically employed in refrigeration systems, air conditioning units, and industrial processes requiring both heating and cooling. Its ability to provide high heat transfer capacity and durability makes it a preferred choice over other types of heat exchangers.
Why Are Finned Tubes Made of Aluminum?
Aluminum finned tubes come in sizes ranging from 3/8†to 1 1/2â€.
Aluminum is extensively used for manufacturing finned tubes because of its unique properties:
- Excellent thermal conductivity
- Lightweight design
- Strong corrosion resistance
- Flexibility and malleability
- Economical cost
Finned Tube Heat Exchanger Working Principle

Finned tube heat exchangers primarily function by transferring heat from one fluid to another via the tubes, enhanced by the fins that boost heat transfer efficiency.
Low Fin Tube Has a Fin Height of Approximately 1/16th Inch
A low fin tube is an individual tube crafted from a particular material featuring a minor fin height of roughly 1/16th of an inch. The fin resides within the tube wall barrier. It is commonly utilized in applications involving liquid-to-liquid or liquid-to-gas purposes, such as coolers, chillers, and condensers.
Low Fin Tubes Dimensions
| Description |
Size Dimension |
| Tubular Outside Diameter |
Minimum 12.7mm / Maximum 31.75mm |
| Tubular Thickness (Plain Section) |
Minimum 1.245mm / Maximum 3.404mm |
| Fin Pitch |
19 - 26 - 27 - 28 - 30 - 36 fins per inch |
| Fin Height |
Maximum 1.40mm |
| Tubular Length |
Maximum 25000mm |
Welded Helical Solid Finned Tubes Widely Used in Petrochemical Industry
These tubes offer resistance to corrosion, high-pressure conditions, and extreme temperatures. Consequently, they are utilized in the petrochemical sector or industrial boilers where such conditions are frequently encountered. They serve to heat or cool or enhance heat recovery from industrial exhausts.
Applications of Helical Solid Finned Tubes
- Petrochemical Industries
- Natural Gas Processing
- Blast Furnace and Converter Systems
- Power Generation
- Waste Incinerators
- Air Conditioning
- Compressor Coolers
Advantages of Using Fin and Tube Heat Exchangers
- Enhances Heat Transfer Rates
- Improves Heat Transfer Coefficients
- Reduces Equipment Size
- Makes Projects Cost-Efficient
- Increases External Surface Area
Features of G-Type Finned Tubes
- High Fin Stability
- Superior Heat Transfer Efficiency
- Increased Operating Temperature Capability
- Rugged Temperature Resistance
- Exceptional Thermal Shock Resistance
Quality Control for Stainless Steel Finned Tubes
- Chemical Composition Analysis
- Dimensional Inspection
- Flattening Test
- Non-Destructive Testing
- Hydrostatic Testing
- Mechanical Property Evaluation
- Expansion Testing
- Surface Quality Assessment
Size Range of G-Type Fin Tubes
| Base Tube Specifications |
Fin Specifications |
| Outer Diameter (mm) |
Wall Thickness (mm) |
Height (mm) |
Thickness (mm) |
Pitch (mm) |
| 15.88-50.8 |
1.0-3.0 |
6.35-25.4 |
0.4 |
2.1-6.0 |
| Material |
Material |
Length |
| SS, CS, Alloy Steel, Copper |
CS, Aluminum, Copper |
≤ 15m |
Classification of Finned Tubes Based on Process and Fin Shape
| Tubular Outer Diameter |
Fin Thickness |
Fin Height |
Fins per Pitch |
| 5/8 |
.015 / .016 / .020 |
3/8, 1/2 |
6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 |
| 3/4 |
5/8, 1/2 |
| 1 |
5/8, 1/2 |
| 1 1/4 |
5/8, 1/2 |
| 1 1/2 |
5/8, 1/2 |
Finned Tubes Typically Use Air to Cool or Heat Fluids Like Water
Finned tubes significantly increase the surface area of the tubes, leading to more efficient heat transfer with air. Utilizing air for heating or cooling is advantageous since it is readily available, cost-effective, and eliminates the need for complex heating equipment or labor-intensive tools.
High Fin Tubes vs. Low Fin Tubes
| Features |
High Fin Tubes |
Low Fin Tubes |
| Fin Density |
Higher fin density |
Lower fin density |
| Heat Transfer Efficiency |
Superior heat transfer efficiency due to higher fin density |
Lower heat transfer efficiency compared to high finned tubes |
| Surface Area-to-Volume Ratio |
Higher surface area-to-volume ratio due to fin density |
Lower surface area-to-volume ratio due to modest fin density |
| Maintenance and Cleaning |
Requires more maintenance and cleaning due to closely spaced fins |
Less maintenance needed compared to high fin tubes due to more spaced-out fins |
| Cost Considerations |
More expensive due to complex manufacturing processes and materials |
Cost-effective |
What Can Cause Leaks in Low Fin Tubes?
- Scale Buildup: This narrows the inner diameter of the tube, causing pressure buildup and eventual leakage
- Thermal Shock: Rapid temperature changes can lead to cracks or ruptures
- Improper Installation: Proper installation and regular maintenance can prevent leaks
- Tubular Corrosion: Corroded tubes are prone to leaking
What Affects Heat Transfer in Low Fin Tubes?
Several factors influence the effectiveness and efficiency of heat transfer in these tubes:
- Properties of the fluids involved
- Arrangement of the fins
- Number of fins present
- Dimensions of the fins
- Surface finish quality
2-Piece Can Making Line
2-Piece Can Making Line Combination Machine,Food Juice Tin Can Testing Machine, 2 Piece Cans,Can Body Making Production Line
Zhoushan Longwen Machinery Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.longwenmachinery.com








